About Me
Applied ML Researcher (Ph.D.) with expertise in multispectral satellite imagery and physics-guided deep learning. Expert in developing segmenting and predictive models for complex physical systems, supported by a strong foundation in MLOps, CI/CD, and GPU-accelerated infrastructure. Formerly a Research Intern at JHU Applied Physics Lab, focusing on one-shot classification and model orchestration.
Education
Ph.D. in Computer Science
University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP)
- Thesis: Physics-Guided Strategies for Enhancing Neural Networks Trained With Limited Data
B.Sc. in Computer Science
University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP)
- Minor in Biomedical Engineering and Mathematics
Experience
Research Assistant and Teaching Assistant
University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP)
- Taught Data Structures, Computer Vision, Deep Learning, and Machine Learning courses
- Developed and trained Deep Q-Network for PowerTAC retail market simulation using Deeplearning4j in Java
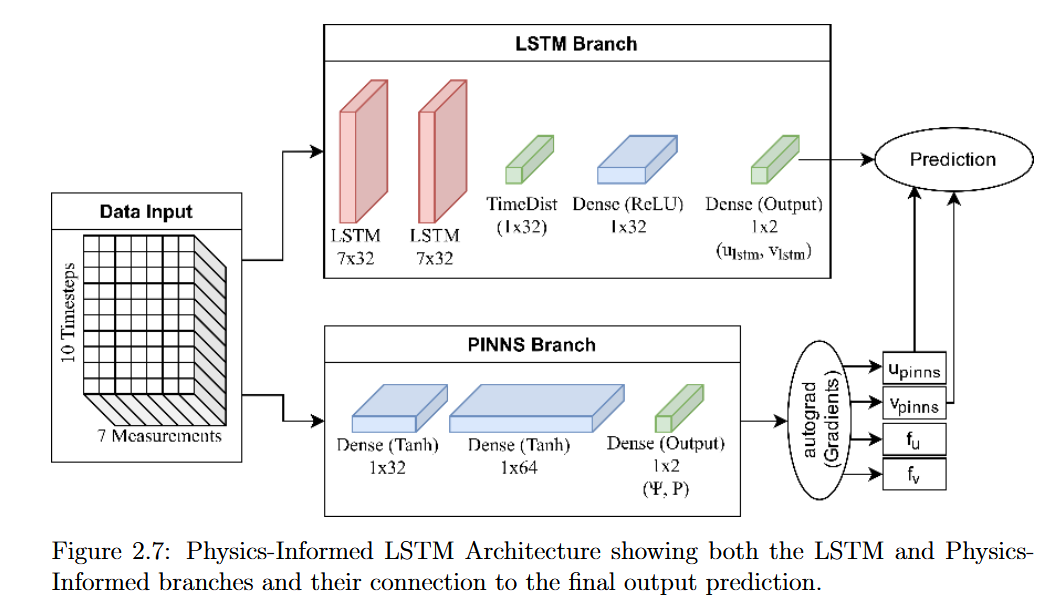
- Developed Physics-Informed LSTMs for fluid flow velocity prediction with PyTorch
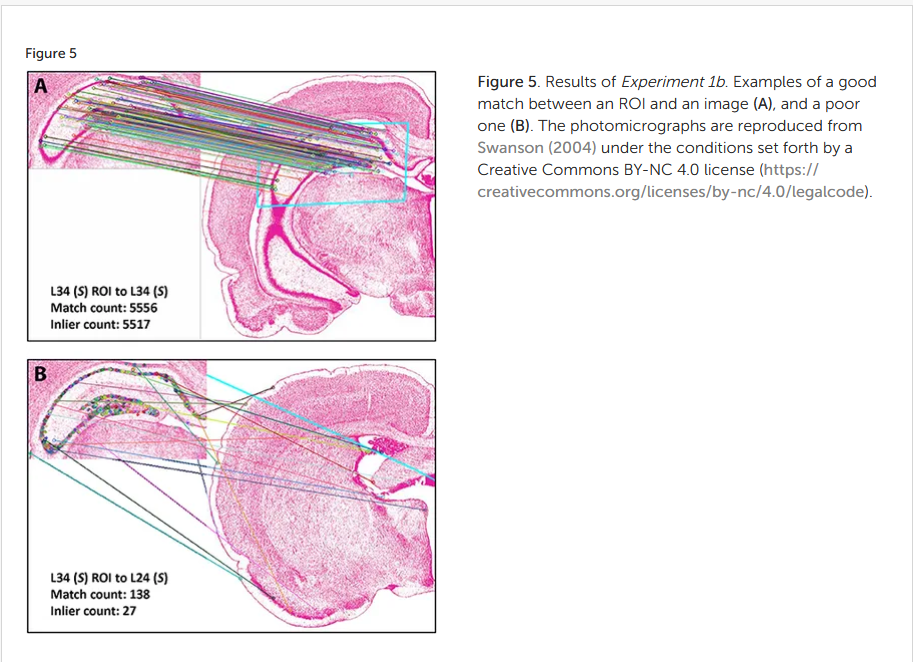
- Developed system mapping rat brain images to labeled atlases using OpenCV with SIFT and RANSAC
- Developed synthetic image generation program using OpenCV multi-point warping
- Configured and maintained Ubuntu servers with NVIDIA GPUs for the research group
Machine Learning Ph.D. Intern for AOS/QAC LIVELab
Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab (APL)
- Trained PyTorch models for multispectral satellite image classification
- Trained Triplet Loss-based PyTorch models for real-time one-shot image classification
- Orchestrated PyTorch models using Prefect for scheduling, coordination, and monitoring
- Created custom Docker images and deployed Prefect using Docker Compose
- Created GitLab CI/CD pipelines for linting, unit testing, and artifact creation
- Developed Streamlit app with prompt engineering using OpenAI ChatGPT models
- Created models for mission-dependency visualization using APL Dagger
Undergraduate Research Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
- Created multiscale model of T cells and APCs interactions using CompuCell3D in Python
Publications
Physics-Informed Glacier Ice Segmentation of HKH Region Using Multispectral Satellite Imagery
J. G. Perez*, O. Fuentes
In Progress
Physics-guided neural network approaches for segmenting glacial ice in multispectral satellite imagery of the Hindu-Kush Himalayan region. Extends PINN concepts to semantic segmentation with limited training data.
Field Predictions of Hypersonic Cones Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks
D. Villanueva, B. Paez, A. Rodriguez, A. Chattopadhyay, V.M. Kotteda, R. Baez, J. G. Perez*, J. Terrazas, V. Kumar
Proceedings of the ASME 2022 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting
Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) provide a way to apply deep learning to train a network using data and governing differential equations that control the physical behavior of a system. We propose using the PINNs framework to solve an inverse problem which will discover the partial differential equations for compressible flow from Mach number = 5 by coupling Navier Stokes Equations with a Deep Neural Network (DNN) based on training data generated by a CFD solver.
Physics-Informed Long-Short Term Memory Neural Network Performance on Holloman High-Speed Test Track Sled Study
J. G. Perez*, R. Baez, J. Terrazas, A. Rodriguez, D. Villanueva, B. Paez, A. Cruz, O. Fuentes, V. Kumar
Proceedings of the ASME 2022 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting
Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) incorporate known physics equations into a network to reduce training time and increase accuracy. Traditional PINNs approaches are based on dense networks that do not consider the fact that simulations are a type of sequential data. We propose a Physics Informed LSTM network that leverages the power of LSTMs for sequential datasets that also incorporates the governing physics equations of 2D incompressible Navier-Stokes fluid to analyze fluid flow around a stationary geometry resembling the water braking mechanism at the Holloman High-Speed Test Track.
Empirical Game-Theoretic Methods to Minimize Regret Against Specific Opponents
M. Porag, J. G. Perez*, C. Kiekintveld, T. Son, W. Yeoh, E. Pontelli
Proceedings of SPIE Defense + Commercial Sensing Symposium
In many real-world multi-domain applications, if there is an opportunity to sense the opponent's strategy from previous rounds, an agent can exploit its opponent in payoffs by playing a specific Best Response (BR) strategy. We propose Clustered Double Oracle Empirical Game-Theoretic Analysis (CDO-EGTA), which builds upon the classic Double Oracle framework based on Deep Q-Network (DQN) and clustering methods. Empirical results show that our method outperforms the current state-of-the-art methods in terms of regret.
Computer vision evidence supporting craniometric alignment of rat brain atlases to streamline expert-guided, first-order migration of hypothalamic spatial datasets
A. M. Khan, J. G. Perez*, C. Wells, O. Fuentes
Frontiers in System Neuroscience
The rat has arguably the most widely studied brain among all animals, with numerous reference atlases for rat brain having been published since 1946. We provide a tool that allows levels from any of the seven published editions of atlases comprising three distinct Paxinos-Watson reference spaces to be aligned to atlas levels from any of the four published editions representing Swanson reference space using computer vision with SIFT and RANSAC.
Projects
Blog
Technical tutorials, guides, and insights from my work.
